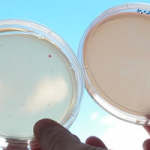
1. Starch Hydrolysis
Medium: Starch Agar
Procedure:
- Obtain pure culture of the bacterium
- Make a single streak line of the bacterium on the starch agar
- Incubate at 37oC for 48-72 hours.
- After the end of the incubation period, iodine is added to see if the starch remains or has been hydrolysed. If the starch has been hydrolysed there will be clear zone around the bacterial growth.
Note: This procedure can be used on multiple bacteria on the same agar plate, you just need to divide the plate with a marker into the number of segments needed and label appropriately. Then make a single line streak with appropriate organism on the corresponding segments of the plate.
2. Fermentation of Carbohydrates
Medium: Tubes of phenol red sugar broth
Procedure:
- Label each tube with the name of the sugar in the tube and the code of the bacterium you are growing
- Inoculate the phenol red sugar broth in the tube containing the Durham tube (used to trap bubble in case of gas production) with the bacterium
- Incubate all tubes at 37oC for 4-7 days
Note: If the particular sugar is fermented by the bacterium, colour change will be observed (phenol red turns yellow). If gas is produced, it collects in the Durham tube as a gas bubble.
3. Catalase Activity
Procedure:
Add a few drops of 3% hydrogen peroxide to each bacterium you are growing on a clean glass slide and look for the release of oxygen as a result of hydrogen peroxide breakdown. This appears as foaming.
References
- Keiser, G.E. ‘Laboratory manual’
- Cain, D., Hanks, H., Weis, M., Bottoms, C., and Lawson J. ‘Microbiology Laboratory Manual Biol 2421L Revised Spring Edition’
Download “Identification of Bacteria through Biochemical Tests”
Identification-of-Bacteria-through-Biochemical-Tests.docx – Downloaded 0 times – 20.34 KB